 |
 |
The TM_TEST function computes the Student's T-statistic and the probability that two sample populations X and Y have significantly different means. X and Y may be of different lengths. The result is a two-element vector containing the T-statistic and its significance. The significance is a value in the interval [0.0, 1.0]; a small value (0.05 or 0.01) indicates that X and Y have significantly different means. The default assumption is that the data is drawn from populations with the same true variance. This type of test is often referred to as the t-means test.
The T-statistic for sample populations x and y with means ` x and ` y is defined as:
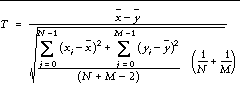
where x = ( x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , ..., x N-1 ) and y = ( y 0 , y 1 , y 2 ..., y M-1 )
This routine is written in the IDL language. Its source code can be found in the file
tm_test.pro
in the
lib
subdirectory of the IDL distribution.
Define two n -element sample populations.
X = [257, 208, 296, 324, 240, 246, 267, 311, 324, 323, 263, $
305, 270, 260, 251, 275, 288, 242, 304, 267]
Y = [201, 56, 185, 221, 165, 161, 182, 239, 278, 243, 197, $
271, 214, 216, 175, 192, 208, 150, 281, 196]
Compute the Student's t-statistic and its significance assuming that X and Y belong to populations with the same true variance.
The result indicates that X and Y have significantly different means.