 |
 |
The VOIGT function returns the intensity of an atomic absorption line profile (also known as a VOIGT profile) based on the Voigt damping parameter a and the frequency offset u, in units of the Doppler width. The result is always floating-point and has the same structure as the arguments. Note that a and u should not both be vectors.
The returned line profile f ( a , u ) is defined as:

where H is the classical Voigt function:

The Doppler width D v D (assuming no turbulence), is defined as:
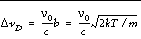
where n 0 is the line center frequency. The dimensionless frequency offset u and the damping parameter a are determined by:
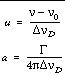
Here, G is the transition rate:

where g is the spontaneous decay rate, and n col is the atomic collision rate. See Radiative Processes in Astrophysics by G. B. Rybicki and A. P. Lightman (1979) p 291 for more information. The algorithm is from Armstrong, JQSRT 7 , 85. (1967).